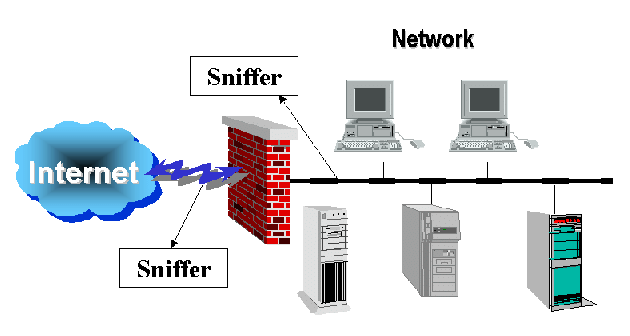
What is packet sniffer?
Packet sniffing is the practice of gathering, collecting, and logging some or all packets that pass through a computer network, regardless of how the packet is addressed. In this way, every packet, or a defined subset of packets, may be gathered for further analysis. A packet sniffer, sometimes called a packet analyzer, is composed of two main parts. First, a network adapter that connects the sniffer to the existing network. Second, software that provides a way to log, see, or analyze the data collected by the device.
How does packet sniffing work?
A network is a collection of nodes, such as personal computers, servers, and networking hardware that are connected. The network connection allows data to be transferred between these devices. The connections can be physical with cables, or wireless with radio signals. Networks can also be a combination of both types.As nodes send data across the network, each transmission is broken down into smaller pieces called packets. The defined length and shape allows the data packets to be checked for completeness and usability. Because a network’s infrastructure is common to many nodes, packets destined for different nodes will pass through numerous other nodes on the way to their destination.A packet’s address is examined by each network adapter and connected device to determine what node the packet is destined for. Under normal operating conditions, if a node sees a packet that is not addressed to it, the node ignores that packet and its data.